You will notice that stockholder’s equity increases with commonstock issuance and revenues, and decreases from dividend payoutsand expenses. Stockholder’s equity is reported on the balance sheetin the form of contributed capital (common stock) and retainedearnings. The expanded accounting equation is a form of the basic accounting equation that includes the distinct components of owner’s equity, such as dividends, shareholder capital, revenue, and expenses. The expanded equation is used to compare a company’s assets with greater granularity than provided by the basic equation. Some common examples of assets are cash, accounts receivable, inventory, supplies, prepaid expenses, notes receivable, equipment, buildings, machinery, and land. Some commonexamples of assets are cash, accounts receivable, inventory,supplies, prepaid expenses, notes receivable, equipment, buildings,machinery, and land.
- The accounting equation emphasizes a basic idea in business; that is, businesses need assets in order to operate.
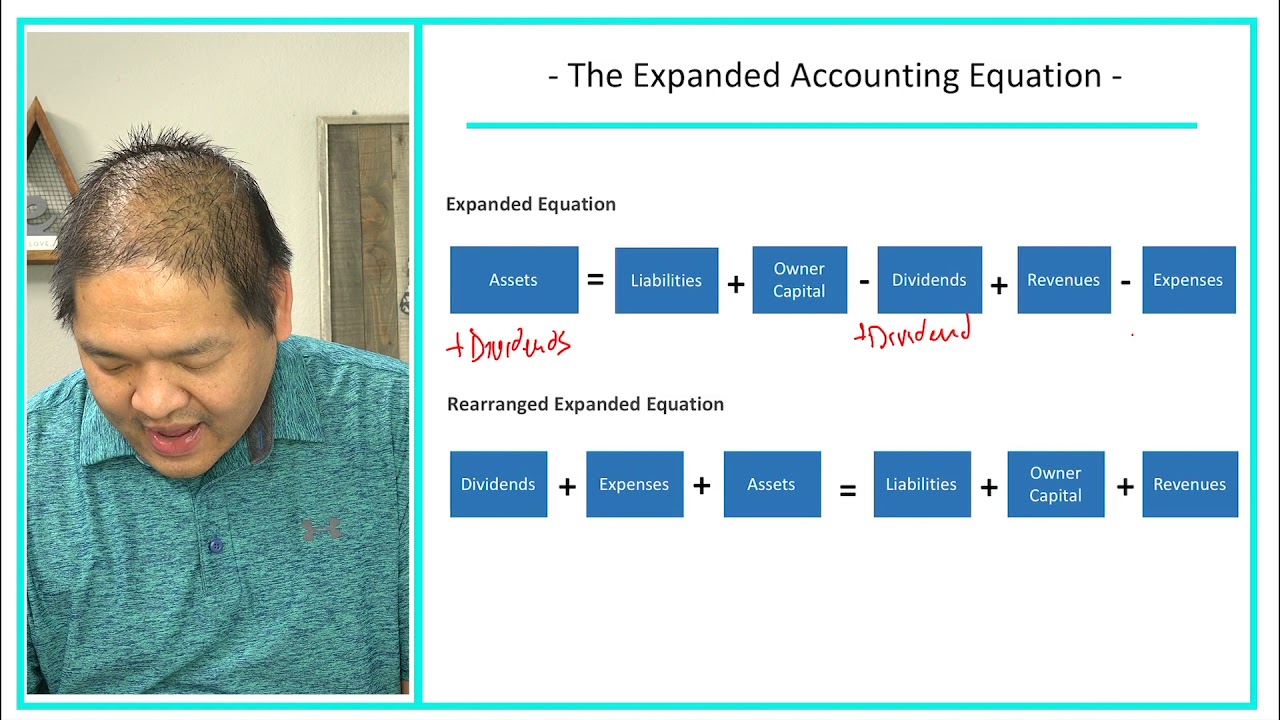
- The expanded accounting equation is defined as assets being equal to liabilities plus the contributed capital, retained earnings at the beginning of the period, revenues, and less expenses and dividends.
- It is an important concept from the accounting point of view because it provides a picture of the organization’s financial well-being.
- First, it can sell shares of its stock to the public to raise money to purchase the assets, or it can use profits earned by the business to finance its activities.
Expanded accounting equation
Remember, when a customer purchases something “onaccount” it means the customer has asked to be billed and will payat a later date. Equipment examples include desks, chairs, and computers;anything that has a long-term value to the company that is used inthe office. Equipment is considered a long-term asset, meaning youcan use it for more than one accounting period (a year forexample). Equipment will lose value over time, in a process calleddepreciation.
Advantages of the Expanded Accounting Equation
We could also look to XOM’s income statement to identify the amount of revenues and dividends the company earned and paid out. An important thing to remember is that revenues increase equity while expenses and owner’s withdrawals decrease it. So, your regular income-related transactions involve these elements in addition to assets or liabilities. Gain better visibility into your profits and shareholder investments using this nifty tool.
Are You Ready to Take Your Accounting Skills to the Next Level on the Information Highway?
The Expanded Accounting equation is generally different for varying forms of businesses. The equation differs slightly in the case of a proprietary concern, partnership firm, and corporation. My Accounting Course is a world-class educational resource developed by experts to simplify accounting, finance, & investment analysis topics, so students and professionals can learn and propel their careers. Shaun Conrad is a Certified Public Accountant and CPA exam expert with a passion for teaching. After almost a decade of experience in public accounting, he created MyAccountingCourse.com to help people learn accounting & finance, pass the CPA exam, and start their career.
Resources
For the past 52 years, Harold Averkamp (CPA, MBA) has worked as an accounting supervisor, manager, consultant, university instructor, and innovator in teaching accounting online. Some terminology may vary depending on the type of entity structure. « Members’ capital » and « owners’ capital » are commonly used for partnerships and sole proprietorships, respectively, while « distributions » and « withdrawals » are substitute nomenclature for « dividends. »

Accounting made easy, for FREE!
Thus, there are resources with offsetting claims against those resources, either from creditors or investors. All three components of the accounting equation appear in the balance sheet, which reveals the financial position of a business as of the date stated on the document. Equity increases from revenues and owner investments (stock issuances) and decreases from expenses and dividends. Another component of stockholder’s equity is company earnings.These retained earnings are what the company holds onto at the endof a period to reinvest in the business, after any distributions toownership occur. Stated more technically, retained earnings are acompany’s cumulative earnings since the creation of the companyminus any dividends that it has declared or paid since itscreation. One tricky point to remember is that retained earningsare not classified as assets.
Organizations use the equation to understand a holistic and descriptive financial statement picture. It can be used for deep diving into the organization’s financial transactions, thereby also in the detailed analysis of the financial statements. This results in the movement of at least two accounts in the accounting equation. The amount of change in the left side is always equal to the amount of change in the right side, thus, keeping the accounting equation in balance.
Accounts payable recognizes that the company owes money and has not paid. Remember, when a customer purchases something “on account” it means the customer has asked to be billed and will pay at a later date. Equipment examples include desks, chairs, and computers; anything that has a long-term value to the company that is used in the office.
The difference between the revenue and profit generated and expenses and losses incurred reflects the effect of net income (NI) on stockholders’ equity. Overall, then, the expanded accounting equation is useful in identifying proforma invoice template at a basic level how stockholders’ equity in a firm changes from period to period. When a company first starts the analysis process, it will make alist of all the accounts used in day-to-day transactions.
Some common examples of liabilities includeaccounts payable, notes payable, and unearned revenue. Recall that the basic components of even the simplest accountingsystem are accounts and a general ledger. Accounts shows all thechanges made to assets, liabilities, and equity—the three maincategories in the accounting equation. Each of these categories, inturn, includes many individual accounts, all of which a companymaintains in its general ledger. This equation represents your company’s reality in terms of its economic resources (assets), obligations (liabilities), and residual ownership claims (ownership equity). From this, you can assess how efficiently your business is turning revenues into profits and absorbing expenses.

